The process can be initiated in a number of ways but most commonly involves the presence of species which decompose into radicals known as.
Free radical polymerization of vinyl monomers.
The free radical then reacts with a vinyl monomer that is.
One of the most common and useful reaction for making polymers is free radical polymerization.
It is used to make polymers from vinyl monomers that is from small molecules containing carbon carbon double bonds.
Free radical polymerization frp is one of the most important synthesis routes for obtaining vinyl polymers.
Free radical polymerization frp is a type of chain growth polymerization where the polymer is formed by successive addition of building blocks vinyl monomers to a propagating radical chain 1 2.
Free radical polymerization frp is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free radical building blocks.
To realize polymer electrolytes with high ionic conductivity we exploited the high ionic conductivity of an ionic liquid.
In situ free radical polymerization of compatible vinyl monomers in a room.
The relatively non specific nature of the free radicals towards vinyl and other unsaturated monomers makes frp one of the most versatile polymerization methods.
It is used to make polymers from vinyl monomers.
One of the most common and useful reactions for making polymers is free radical polymerization.
Polymers made by free radical polymerization include polystyrene.
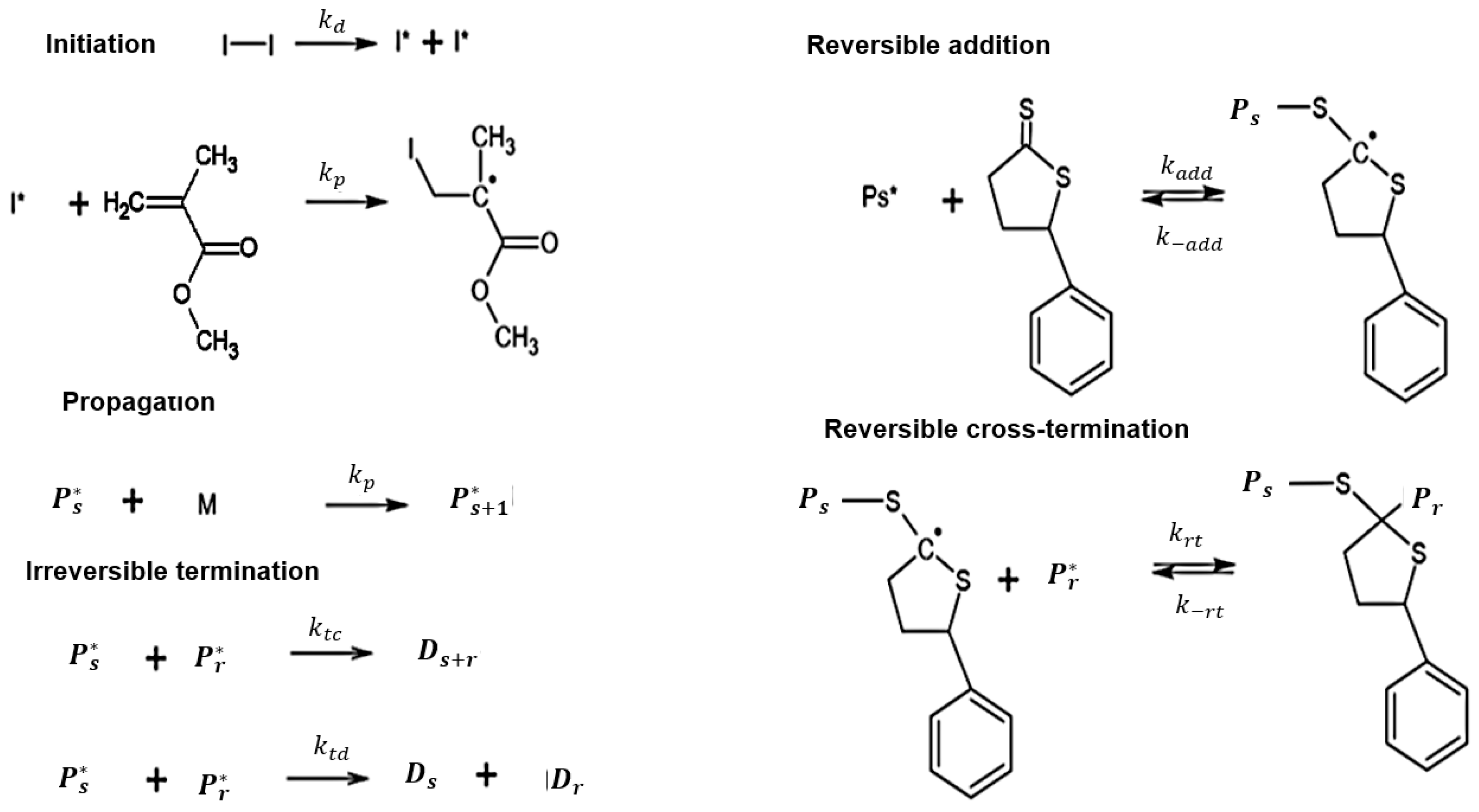
Following its generation the initiating free radical adds nonradical monomer units thereby growing the polymer chain.
Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules.
That is from small molecules containing carbon carbon double bonds.
Mechanism of free radical polymerization.
Propagation is the rapid and progressive addition of monomers to the growing polymer chain without a change of the active center.
Free radical polymerization of vinyl monomers.
Free radical polymerization consists of three fundamental steps initiation propagation and termination.
Since this can be initiated by traces of oxygen or other minor impurities pure samples of these compounds are often stabilized by small amounts of radical inhibitors to avoid unwanted reaction.